By how much is Earth warming?
Global warming is largely determined by the volumes of greenhouse gases being emitted now and in the future. The climate is currently changing at an extremely high pace. The paragraphs below explain by how much temperatures have risen worldwide and in the Netherlands, and by how much Earth will continue to warm.
How much have average temperatures risen by now?
According to the KNMI, worldwide average temperatures have risen by 1.4 °C since 1880. The bulk of this rise has occurred after 1996; since then, temperatures have been rising by 0.3 °C every ten years.
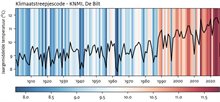
How much warmer is it currently in the Netherlands?
In the Netherlands, temperatures have risen even more than the worldwide average, due to changes in local weather conditions. For example, more frequent western winds have resulted in milder winters, whilst an increase in solar radiation has led to extremely hot summers. The latter is mainly the result of declining air pollution. The KNMI climate dashboard shows that since 1901 average temperatures in our country have risen by 2,6 °C. The dashboard further shows that “the norm” is going up increasingly further. This means, for example, that a temperature that used to be considered normal is now perceived as quite cold. In January 2021, KNMI established an average annual temperature of 10.5 °C as the new normal for the period 1991-2020. This is the benchmark for the current climate. In the period 1901-1930, this value still stood at 8.9 °C.
How much warmer will it be in the future?
Further global warming depends on greenhouse gas emissions. However, even if we manage to reduce emissions significantly, the temperature will continue to rise until at least 2050. According to the sixth IPCC report, the odds are that global temperature will rise by more than 1.5 °C to 2 °C this century. The highest emission scenario even indicates that temperatures will have risen by between 3.3 °C and 5.7 °C by the end of this century. In all the KNMI climate scenarios, average temperatures in the Netherlands will continue to rise in the years ahead. In the most extreme scenario, the average temperature rises to 12.1°C in 2050 and to 14.8°C in 2100.
How does KNMI develop the climate scenarios?
Since 1995, KNMI has been developing climate scenarios once every few years, by commission of the Ministry of Infrastructure and Water Management. The most recent KNMI scenarios were published in 2023. These scenarios translate the global IPCC climate projections to the Dutch situation, including the Caribbean Netherlands. They were calculated using the latest climate models that describe four pathways of a possible future climate in the Netherlands around 2050, 2100 and 2150, based on a low and a high greenhouse gas emission scenario.